Peanut Pod Rot
Many farmers have reported Peanut Pod Rot, which is a major headache. Once Peanut Pod Rot occurs, it has a significant impact on yield and quality, and in severe cases, it can even lead to total crop failure. Today, we will discuss in detail the prevention and treatment of peanut fruit rot.
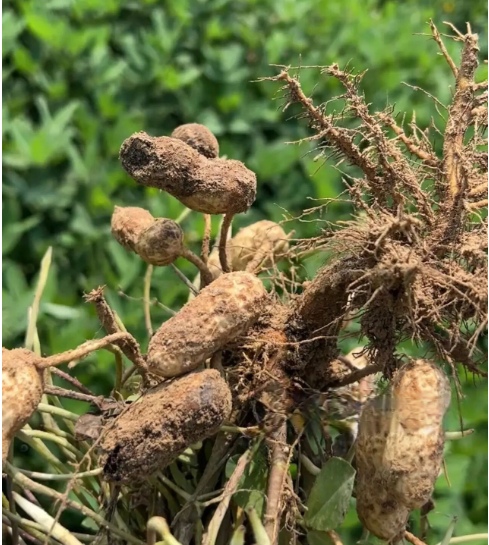
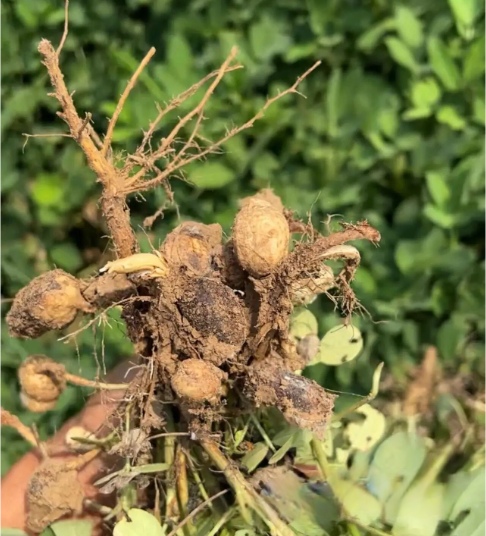
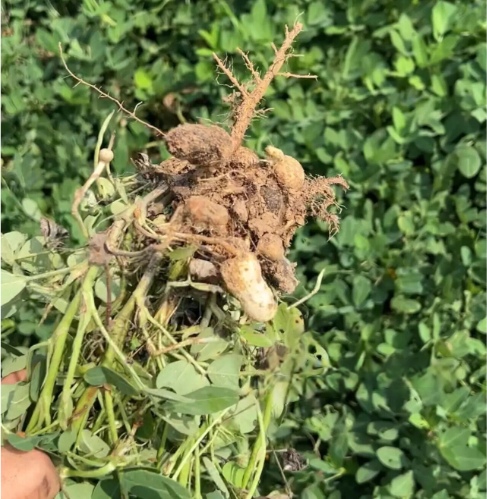



I. Understanding Peanut Pod Rot
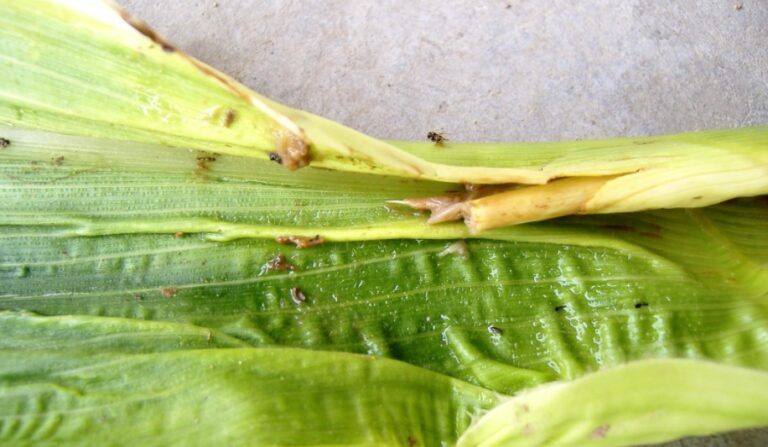
Peanut pod rot, also known as “peanut fruit rot,” can occur from the pod-setting stage to harvest. When infected, the peanut pod rots. In mild cases, half of the pod turns brown or black, the kernel is small and hard, poorly developed, and the shell turns yellow. In severe cases, the entire pod turns dark black, and both the shell and kernel rot completely. It usually occurs on the entire plant or in patches. If the pod stalk is affected and turns black and rots, it can easily cause the pod to fall off or sprout.
2.Causes of the Disease
(1)Pathogen Infection: Fusarium and other fungi, along with some bacteria, directly attack peanut pods through soil, plant debris, or seeds and cause rot. Continuous cropping quickly builds up these pathogens in the soil and greatly increases disease risk. For example, growing peanuts in the same field for several years sharply raises the number of harmful pathogens and makes peanut fruit rot more likely.
(2)Soil problems: When the soil is calcium deficient, peanuts cannot absorb enough calcium, causing the shells to fail to calcify, becoming loose and defective, making them susceptible to pathogen infection. Soil acidification and compaction, coupled with heavy rainfall later in the season, or excessive watering after a prolonged period of high temperature and drought, will reduce soil aeration, exacerbating peanut rot.
(3)Damage from underground pests: When underground pests such as grubs gnaw on the pods or stems, they leave wounds through which pathogens can easily enter, leading to peanut rot.
(4)Improper field management: Applying too much nitrogen fertilizer or uncomposted organic fertilizer weakens peanut plant growth and lowers their disease resistance. Sowing too deep can damage pegs mechanically, making pods more prone to infection. Overwatering, especially during the pod-expansion stage, raises soil moisture and promotes pathogen growth.
Prevention is key for peanut pod rot. Farmers should perform various management tasks during planting and take preventative measures in advance. Once the disease appears, growers should treat it promptly to minimize losses. The control measures for peanut root rot are as follows:
1.Protection and prevention methods
In peanut production, growers protect and prevent diseases by choosing high and dry plots, using high-ridge cultivation, reducing irrigation, applying more calcium fertilizer, removing pathogen sources, and relying on accurate disease forecasting.
2.Seed treatment is currently the most effective method for controlling peanut root rot
In areas where peanut root rot is severe, before sowing, peanut seeds should be coated with a Pyraclostrobin + Metalaxyl-M seed treatment suspension. Before coating, turn the agent into a slurry and use a mixer or coating machine to mix it evenly with the seeds. Let it dry before use. Note that coating should be done immediately before sowing and should not be exposed to direct sunlight to avoid photodegradation and reduced efficacy.
In areas where peanut root rot and grubs occur together, peanut seeds should be coated with a seed treatment suspension of Difenoconazole + Fludioxonil + Thiamethoxam or Pyraclostrobin + Flonicamid + Clothianidin before sowing. Spread the seeds out in a cool, ventilated place to dry, and sow them promptly. Users should apply the prepared solution within 24 hours.